Fat Facts Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids
Energy-rich fats provide fuel for your day-to-day functioning. Lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds mainly composed of hydrocarbon chains.

Fatty Acid Definition Structure Functions Properties Examples Britannica
Fats are the fatty acid esters of glycerol and are the primary energy depots of animals.

. Jayant Science Department Borough of Manhattan Community College City University of New York Tis case study focuses on the structure and function of diferent fat molecules such as fatty acid triacylglycerol. Nevertheless they can be synthesized from the biosynthetic pathways. These fatty acids appear to play distinctive roles in the structure and function of biologic membranes in the retina and central nervous system Neuringer and Connor 1986.
These are the molecule that make up the plasma membrane or cell membrane of cells. NATIO NAL CENTER FOR CASE STUDY TEACHING IN SCIENCE Fat Facts. Lipids are a class of compounds characterised by their solubility in nonpolar solvents and insolubility in water.
Anabel Ramírez 1098651 Mariel Reyes 1100582. Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids. Fatty acid chains that do contain double bonds.
Jayant Science Department Borough of Manhattan Community College City University of New York This case study focuses on the structure and function of. Depending on their structure fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated. This case study focuses on the structure and function of different fat molecules such as fatty acid triacylglycerol glycerophospholipid HDL and LDL cholesterols.
All of the following statements are true about lipids EXCEPT that _____. 20 Lipids are insoluble in water. In addition to their structural function in lipids fatty acids are important substrates for energy generation and present an important alternative to glucose.
Fats are divided into unsaturated fats and saturated fats. These vitamins dissolve in fat droplets. View Homework Help - Fat Facts Directions from BIO 160IN at Pima Community College.
This increases the chances of developing cardiovascular disease. Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids Tiscase study focuses on the structure and function of different fat molecules such as fatty acid triacylglycerol glycerophospholipid HDL and LDL cholesterolsThestory also compares the structures and melting points of the paired fatty acids the saturated with unsaturated monounsaturated with. Fatty acids are also used for the synthesis of neuromodulatory lipids eg prostaglandins.
They make up the building blocks of structure and function of living cells. All lipids are fats. Saturated fats raise LDL low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in the blood.
Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids by Ling Chen and Lalitha S. Lipids Like carbohydrates lipids are composed of carbon hydrogen and oxygen atoms but lipids have fewer oxygen atoms and a significantly greater proportion of carbon and hydrogen bonds. View fat_factspdf from CBQ 201 at Instituto Tecnológico de Santo Domintgo.
To supplement curcumin with piperine take 500 mg of the former with 5-67 mg of the latter thrice a day ie 1500 mg. CiteSeerX - Document Details Isaac Councill Lee Giles Pradeep Teregowda. Lipids are hydrophobic in nature.
Unsaturated fats lower LDL levels and reduce the risk of disease. Hence many fatty acids are also called carboxylic acids. Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids by Ling Chen.
Fatty acids that need to be provided by diet are referred to as essential fatty acids. Phospholipids glycerol molecule with two non-polar fatty acid tails and a polar head plus an organic molecule Steroids primarily used in cell membranes as a lipid bilayer Steroids are lipids composed of ringed carbon molecules Typically composed of 4. Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids by Ling Chen and Lalitha S.
Trans fats and cis fats come under the category of unsaturated fats. The energy depots are used for storing energy that may be required by the body. NATIONAL CENTER FOR CASE STUDY TEACHING IN SCIENCE Fat Facts.
Your body also relies on fat to absorb certain nutrients such as vitamins A D E and K. Two types of biological building-block lipids are isoprene groups and ketoacyl. Fats have become synonymous with lipids but they are a sub-group of lipids and are known as triglycerides.
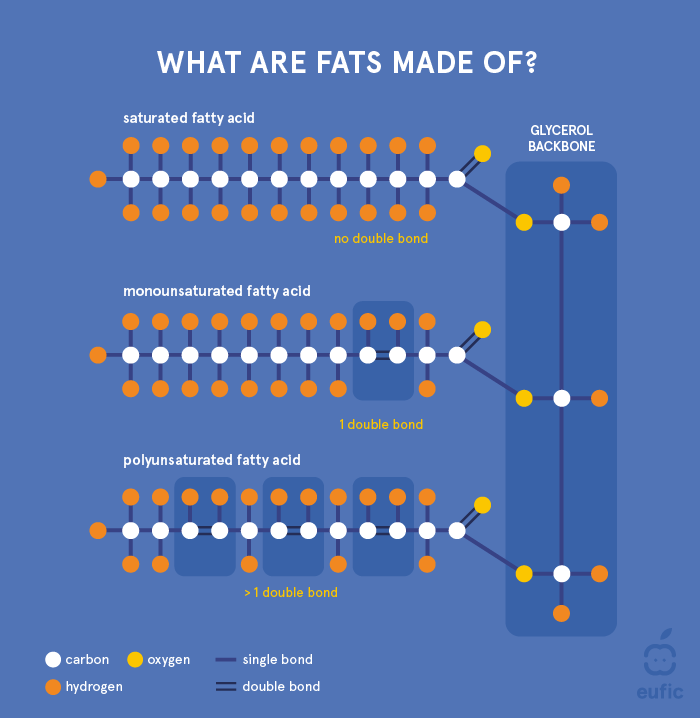
Unsaturated fatty acids form geometric isomers ie the carbon chains are on the same side of the double bond in a cis isomer and on opposite sides of the bond in a trans. This actually means that they will. The story also compares the structures and melting points of the paired fatty acids the saturated with unsaturated monounsaturated with polyunsaturated cis- with trans-isomers.
They form various structures such as liposomes membranes or vesicles with its amphiphilic nature. Lipids are energy-rich organic molecules which provide energy for different life processes. For example vitamin A plays an essential role in maintaining a healthy neurological function vision and healthy skin.
Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids by Ling Chen and Lalitha S. These fats tend to be more soft or liquid like oils. Lipid molecules that contain three fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol backbone.
Lipids are good at. Lipids are biological molecules that are insoluble in water. Fatty acids normally have a long hydrocarbon chain with even numbers of carbon atoms for example 14 16 and 18 and a carboxylic acid functional group -COOH.
Fatty tissue also acts as insulation to help regulate your body temperature and fat cushions your organs to protect them from damage. NATIONAL CENTER FOR CASE STUDY TEACHING IN SCIENCE Fat Facts. Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids.
19 Fat helps the body absorb some vitamins better like vitamins A D E and K. Describe the structure of fatty acids. Draw the structure of the cerebroside that has myristic.

Functions Of Lipids Biochemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry Notes
Functions Classification And Characteristics Of Fats Eufic

All About Lipids Fats And Oils Biochemistry Notes Anatomy And Physiology Physiology

No comments for "Fat Facts Comparing the Structure and Function of Lipids"
Post a Comment